How is cardiac catheterization performed?
Cardiac catheterization is a surgical procedure performed by specialized doctors. It is also called percutaneous coronary intervention. The cardiac catheterization process aims to diagnose the cardiac arteries, which supply the heart with blood so that it can perform its work properly, as these arteries can become blocked or narrow, which leads to a decrease in the rate of blood flow in the arteries.
The reasons for doing it are:
Reducing symptoms of vascular occlusion, These symptoms are chest pain and shortness of breath.
Having a heart attack, as the catheter rapidly opens blocked arteries.
Better heart performance.
Saving the patient’s life, especially if the blockage is large in the artery, which leads to damage to a large part of the heart muscle.
Treating a congenital heart defect such as valve defects, or in the ventricular or atrial septum.
Accurately measure blood pressure in different parts of the heart and lungs.
How it works:
The specialist doctor enters the patient to the hospital one day before the date of the operation to perform some necessary analyzes and x-rays. On the next day, which is the day of the operation, the patient is given local anesthesia to the area of the thigh, arm or wrist, but most of the time the operation is done through the thigh.
Then the doctor purifies the area with antiseptic and covers the whole body with a sterile material and anesthetizes the thigh with a local anesthetic only. The patient is kept awake during the course of the operation, but the patient is given some intravenous medications to help him relax, then negative electrodes are placed on his chest.
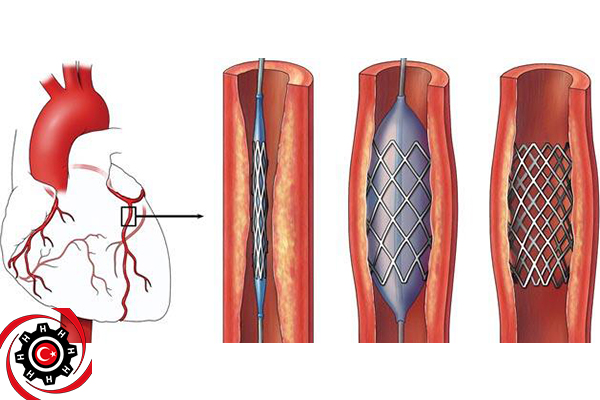
This is in order to monitor the heartbeat during the operation, after which the doctor makes a small incision, then a small and thin tube called the Qantar is inserted through an artery from the thigh. The doctor passes the tube into the main blood vessels until it reaches the coronary arteries in the heart, and during that special cameras photograph the blood vessels The doctor injects a special substance into the coronary arteries of the heart or into the left ventricle. Blood pressure is also measured in the heart. Often in cardiac catheterization operations, the doctor resorts to placing grids or stents in the narrowed arteries after opening them, to help keep the arteries open. These grids are usually coated with a drug that helps To keep the arteries open, at the end of the procedure, the doctor inflates a small balloon to open the blocked arteries. And the doctor can perform the cardiac catheterization process for the same patient more than once if needed, and the catheterization process does not mean that the patient’s heart has fully recovered, but some instructions must be followed to maintain heart health, such as avoiding smoking and alcoholic beverages and reducing foods that contain a high percentage of fat and cholesterol

Leave a Reply