Knee replacement:
Knee replacement surgery aims to treat cartilage erosion in the knee joint, which often occurs as a result of chronic arthritis, of all kinds, especially osteoarthritis, Which leads to determining the patient’s ability to move the knee joint, The operation depends on replacing the affected joint with an artificial knee joint.
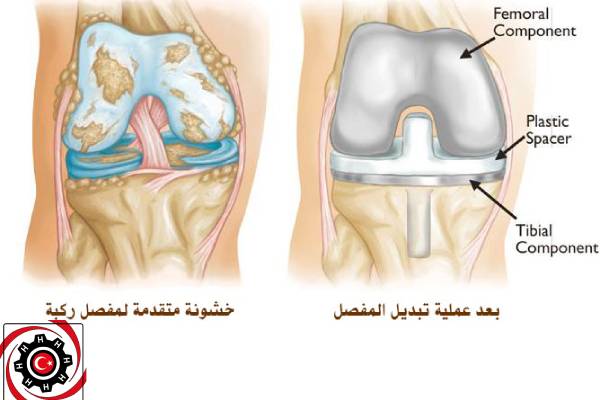
The incidence of osteoarthritis increases with age, where stenosis occurs in the proper articular space, The bone is exposed to the joint cavity.
With the passage of time many pains appear, joint stiffness and marked limitations in movement, Which does not allow the man to move properly while walking.
This operation is performed for patients whose condition does not improve with the help of conservative treatment (exercise, physical therapy or use of anti-inflammatory drugs), And when the patient is unable to carry out his daily activities, which negatively affects the patient’s quality of life.
There are other alternatives to knee replacement surgery, such as arthroscopy or osteotomy, according to the patient’s age and condition of the joint.
Preparing for the operation:
Before performing knee replacement surgery, The patient is sent for examinations as needed. According to the patient’s generation and the diseases he suffers from.
Most of the patients who undergo this operation are relatively elderly. They often need blood tests, which include:
complete blood count, blood chemistry, Blood clotting, urine test, and kidney and liver functions.
ECG and chest x-ray are performed for men over the age of 55 and women over the age of 60.
The doctor sends the patient for an imaging examination of the knee, sometimes the doctor is satisfied with conducting an X-ray examination, but often a computed tomography examination of the knee or magnetic resonance imaging is performed.
Knee joint replacement surgery is performed under general or local anesthesia (spinal / epidural). The surgeon should be consulted about the medications that should be stopped in the days preceding the operation, and one should fast completely for 8 hours before the operation.
The course of the process:
After a thorough sterilization of the operation area, An 8-12 cm long incision is made in the front of the knee.
When exposing the space in the knee joint, The surgeon removes the excess cartilage and bone tissue. that adversely affect the space in the knee joint.
Later, the joint surfaces are modified so that they can contain the plastic-metal artificial joint.
The artificial joint is attached to the femur. tibia and patella, by means of a slurry or other substance, It is used as a physiological adhesive.
Then, The artificial joint is fixed to the knee muscles and ligaments supporting the joint. In order to obtain a motor performance in the joint similar to the normal situation.
The part attached to the femur consists of a hard and smooth metal. Who can bear heavy weights. The joint is covered with an elastic bandage.
Operation risks:
General risks of surgeries:
Infection in the surgical incision is usually superficial and is treated topically. But sometimes a more serious infection can occur in the tissues under the skin and even in the joint itself. Which may require opening the incision again in order to remove bacterial residues.
Bleeding, especially in the surgical area, as a result of local tissue trauma, but, in rare cases, blood meals have to be given.
Bleeding can occur immediately after the operation. Even after 24 hours of the operation, and in very rare cases, bleeding may appear after several weeks or months.
Drainage is needed if there is significant bleeding.
Scars The nature of scar healing is related to the efficacy of surgical sutures and genetic factors. There is no way to predict how scars will heal after surgery.
The dangers of anesthesia Often talk about phenomena related to hypersensitivity to narcotic drugs.
In some rare cases, a severe drop in blood pressure can occur
Special risks:
neurological damage can occur, in rare cases, Due to the great proximity between the joint and the nerves that pass from the spinal cord to the foot.
Damage to ligaments or muscles due to the removal of large parts of the joint, This can sometimes damage soft tissues. Like a wound, muscle tear, or ligament tear.
Fatty embolism when part of the bone marrow separates from the tissue and reaches through the bloodstream to the pulmonary blood vessels and causes them to become obstructed. Fatty embolism can be represented by the appearance of shortness of breath after the operation, which necessitates immediate investigation and treatment, which is rare.
Treatment after the operation:
Patients usually stay in the hospital for several days (3-5 days as needed) after knee replacement surgery.
Pain relievers may be used. If the patient feels pain.
In all cases of pain that does not disappear with the use of painkillers, neurological symptoms such as loss of sensation (numbness) or weakness, headache, body’s temperature raising, Secretions or bleeding from the wound, you must go immediately for a medical examination.
Most patients reported a significant improvement in daily functioning after knee replacement surgery.
This improvement can be seen about a month after the operation.
The pain completely disappears after a few weeks.
move early, That is, the patient’s ability to step on his leg a day after the operation, But you should avoid making sharp movements bending or rotating the knee joint.

Leave a Reply