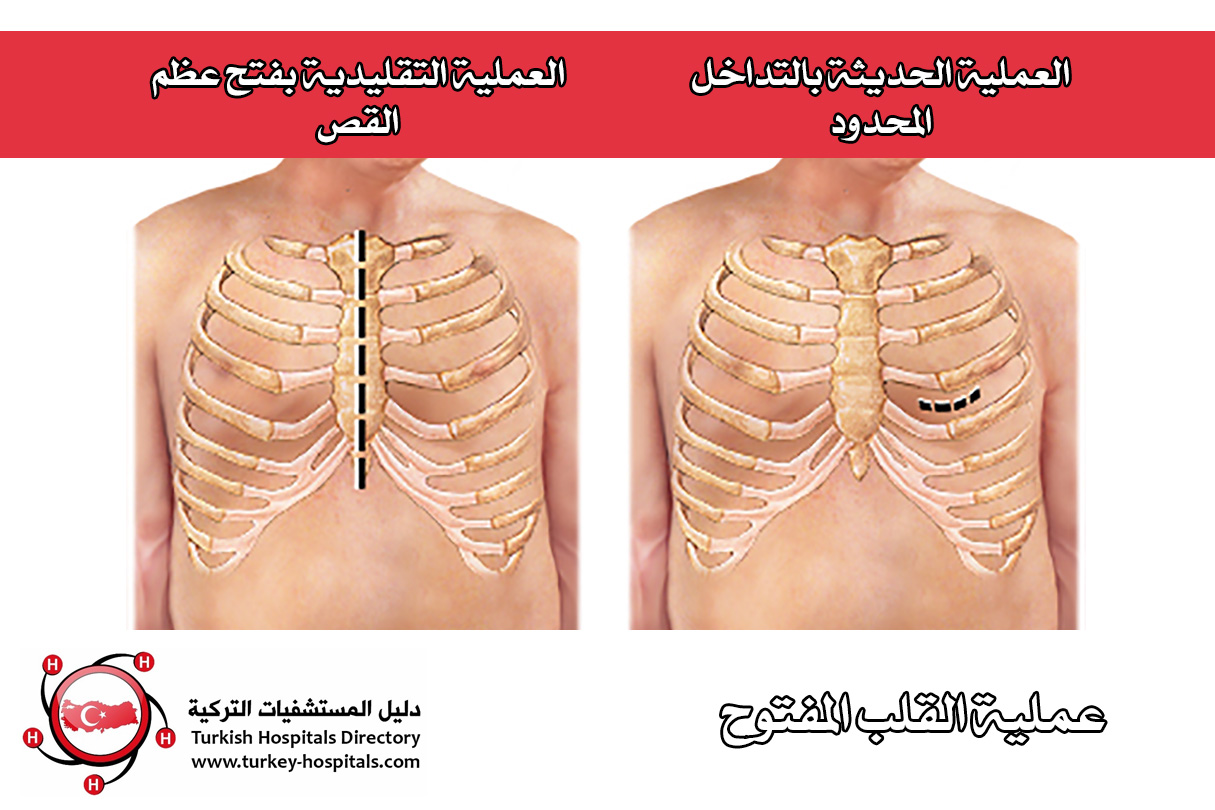
The doctor decides to perform an open-heart surgery after all other treatment methods have run out, such as medications and therapeutic catheters, or the need for a new heart transplant for the patient.
1328

Leave a Reply